Linux Administration Certification Training C ...
- 13k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend
- Live Class
Did you know that more than 90% of the World’s Fastest Computers use Linux? No doubt why! Linux is fast, powerful, and a techies’ favorite. If you are looking to become a Linux Administrator, then this is the right place for you to prepare for the interview. In this article, I will be discussing some of the most common and important Linux Interview Questions and their Answers.
Interested in Linux Administration? Check out the Live Linux Course online.
This Linux Interview Questions blog is divided into two parts: Part A-Theoretical Questions and Part B-Scenario Based Questions. Let’s get started!
In this part of Linux Interview Questions, we will discuss the most common theoretical and concept based questions.
Linux is an Open-Source Operating System based on Unix. Linux was first introduced by Linus Torvalds. The main purpose of Linux was to provide free and low-cost Operating System for users who could not afford Operating Systems like Windows or iOS or Unix.
The main differences between Linux and UNIX are as follows:
| Parameter | Linux | Unix |
| Price | Both free distributions and paid distributions are available. | Different levels of UNIX have a different cost structure |
| Target User | Everyone (Home user, Developer, etc.) | Mainly Internet Server, Workstations, Mainframes. |
| File System Support | Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, Jfs, ReiserFS, Xfs, Btrfs, FAT, FAT32, NTFS. | jfs, gpfs, hfs, hfs+, ufs, xfs, zfs,vxfs. |
| GUI | KDE and Gnome | Common Desktop Environment |
| Viruses listed | 60-100 | 80-120 |
| Bug Fix Speed | Faster because Linux is Community driven | Slow |
| Portability | Yes | No |
| Examples | Ubuntu, Fedora, Red Hat, Kali Linux, Debian, Archlinux, Android, etc. | OS X, Solaris, All Linux |
Linux vs. Unix – Linux Interview Questions
Linux kernel refers to the low-level system software. It is used to manage resources and provide an interface for user interaction.
Yes, it is legal to edit Linux Kernel. Linux is released under the General Public License (General Public License). Any project released under GPL can be modified and edited by the end users.
LILO stands for LInux LOader. LILO is a Linux Boot Loader that loads Linux Operating System into the main memory to begin execution. Most of the computers come with boot loaders for certain versions of Windows or Mac OS. So, when you want to use Linux OS, you need to install a special boot loader for it. LILO is one such boot loader.
When the computer is started, BIOS conducts some initial tests and transfers control to the Master Boot Record. From here, LILO loads the Linux OS and starts it.
The advantage of using LILO is that it allows fast boot of Linux OS.
The basic components of Linux are:
The most common Shells used in Linux are
Swap Space is the additional spaced used by Linux that temporarily holds concurrently running programs when the RAM does not have enough space to hold the programs. When you run a program, it resides on the RAM so that the processor can fetch data quickly. Suppose you are running more programs than the RAM can hold, then these running programs are stored in the Swap Space. The processor will now look for data in the RAM and the Swap Space.
Swap Space is used as an extension of RAM by Linux.
There are 3 main differences between BASH and DOS:
| Sl. no. | BASH | DOS |
| 1. | Commands are case-sensitive. | Commands are not case-sensitive. |
| 2. | ‘/’ (forward slash) is used as a directory separator. ” (backslash) is used as an escape character. | ‘/’ (forward slash) is used as command argument delimiter. ” (backslash) is used as a directory separator. |
| 3. | Follows naming convention: 8 characters for file name postfixed with 3 characters for the extension. | No naming convention. |
Bash vs Dos – Linux Interview Questions
You can use any of the following commands:
free -mvmstattophtopThere are 3 kinds of permission in Linux:
You can change the permission of a file or a directory using the chmodcommand. There are two modes of using the chmod command:
The general syntax to change permission using Symbolic mode is as follows:
$ chmod <target>(+/-/=)<permission> <filename>
where <permissions> can be r: read; w: write; x: execute.
<target> can be u : user; g: group; o: other; a: all
'+' is used for adding permission
'-' is used for removing permission
'=' is used for setting the permission
For example, if you want to set the permission such that the user can read, write, and execute it and members of your group can read and execute it, and others may only read it.
Then the command for this will be:
$ chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r filename
The general syntax to change permission using Absolute mode is as follows:
$ chmod <permission> filename
The Absolute mode follows octal representation. The leftmost digit is for the user, the middle digit is for the user group and the rightmost digit is for all.
Below is the table that explains the meaning of the digits that can be used and their effect.
| 0 | No permission | – – – |
| 1 | Execute permission | – – x |
| 2 | Write permission | – w – |
| 3 | Execute and write permission: 1 (execute) + 2 (write) = 3 | – wx |
| 4 | Read permission | r – – |
| 5 | Read and execute permission: 4 (read) + 1 (execute) = 5 | r – x |
| 6 | Read and write permission: 4 (read) + 2 (write) = 6 | rw – |
| 7 | All permissions: 4 (read) + 2 (write) + 1 (execute) = 7 | rwx |
For example, if you want to set the permission such that the user can read, write, and execute it and members of your group can read and execute it, and others may only read it.
Then the command for this will be:
$ chmod 754 filename
inode is the unique name given by the operating system to each file. Similarly, process id is the unique id given to each process.
There are 5 main Directory Commands in Linux:
pwd: Displays the path of the present working directory.
Syntax: $ pwd
ls: Lists all the files and directories in the present working directory.
Syntax: $ ls
cd: Used to change the present working directory.
Syntax: $ cd <path to new directory>
mkdir: Creates a new directory
Syntax: $ mkdir <name (and path if required) of new directory>
rmdir: Deletes a directory
Syntax: $ rmdir <name (and path if required) of directory>
Virtual Desktop is a feature that allows users to use the desktop beyond the physical limits of the screen. Basically, Virtual Desktop creates a virtual screen to expand the limitation of the normal screen.
There are two ways Virtual Desktop can be implemented:
In the case of Switching Desktops, you can create discrete virtual desktops to run programs. Here, each virtual desktop will behave as an individual desktop and the programs running on each of these desktops is accessible only to the users who are using that particular desktop.
Oversized Desktops do not offer a discrete virtual desktop but it allows the user to pan and scroll around the desktop that is larger in size than the physical screen.
There are 3 modes of vi editor:
A daemon is a computer program that runs as a background process to provide functions that might not be available in the base Operating System. Daemons are usually used to run services in the background without directly being in control of interactive users. The purpose of Daemons are to handle periodic requests and then forward the requests to appropriate programs for execution.
The process states are as follows:
Grep stands for Global Regular Expression Print. The grep command is used to search for a text in a file by pattern matching based on regular expression.
Syntax: grep [options] pattern [files]
Example:
$ grep -c "linux" interview.txt
This command will print the count of the word “linux” in the “interview.txt” file.
The System Calls to manage the process are:
And the System Calls used to get Process ID are:
The ls command is used to list the files in a specified directory. The general syntax is:
$ ls <options> <directory>
For example, if you want to list all the files in the Example directory, then the command will be as follows:
$ ls Example/
There are different options that can be used with the ls command. These options give additional information about the file/ folder. For example:
| -l | lists long format (shows the permissions of the file) |
| -a | lists all files including hidden files |
| -i | lists files with their inode number |
| -s | lists files with their size |
| -S | lists files with their size and sorts the list by file size |
| -t | sorts the listed files by time and date |
The redirection operator is used to redirect the output of a particular command as an input to another command or file.
There are two ways of using this:
‘>’ overwrites the existing content of the file or creates a new file.
‘>>’ appends the new content to the end of the file or creates a new file.
Suppose the content of the file is as follows:
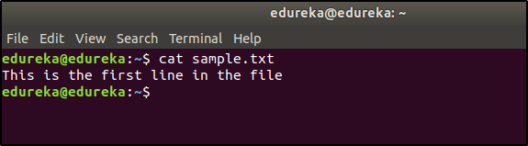
Now when you use the ‘>’ redirection operator, the contents of the file are overwritten.
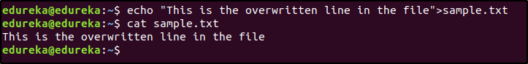
and when you use ‘>>’, the contents are appended:

The tar command is used to extract or create an archived file.
Suppose you want to extract all the files from the archive named sample.tar.gz, then the command will be:
$ tar -xvzf sample.tar.gz
Suppose you want to create an archive of all the files stored in the path /home/linux/, then the command will be:
$ tar -cvzf filename.tar.gz
where c: create archive, x: extract, v: verbose, f: file
A Latch is a temporary storage device controlled by timing signal which can either store 0 or 1. A Latch has two stable states (high-output or 1, and low-output or 0) and is mainly used to store state information. A Latch can store one bit of data as long as it is powered on.
A Microprocessor is a device that executes instructions. It is a single-chip device that fetches the instruction from the memory, decodes it and executes it. A Microprocessor can carry out 3 basic functions:
Regular Expressions are used to search for data having a particular pattern. Some of the commands used with Regular Patterns are: tr, sed, vi and grep.
Some of the common symbols used in Regular Expressions are:
| . | Match any character |
| ^ | Match the beginning of the String |
| $ | Match the end of the String |
| * | Match zero or more characters |
| Represents special characters | |
| ? | Match exactly one character |
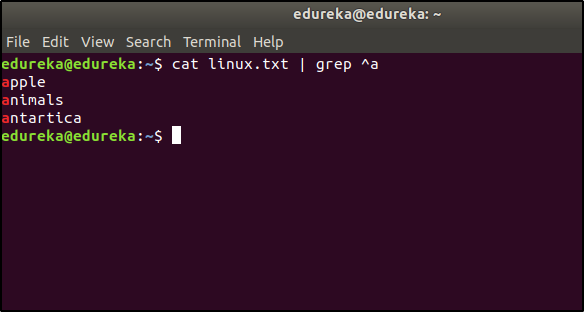
Suppose the content of a file is as follows:

If you want to list the entries that start with the character ‘a’, then the command would be:
$ cat linux.txt | grep ^a
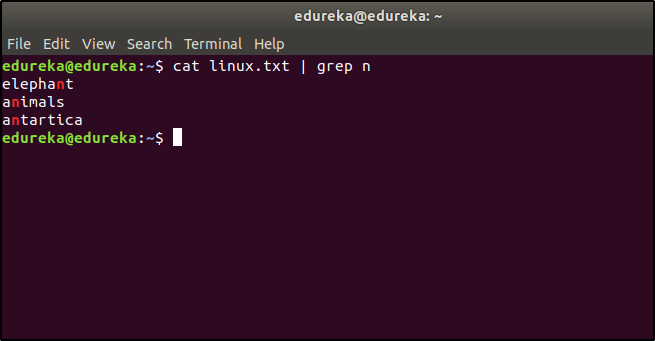
If you want to list the entries that start has the character ‘n’, then the command would be:
$ cat linux.txt | grep n
The minimum number of partitions required is 2.
One partition is used as the local file system where all the files are stored. This includes files of the OS, files of applications and services, and files of the user. And the other partition is used as Swap Space which acts as an extended memory for RAM.
Interviewers will ask scenario based questions along with theoretical questions to check how much hands-on knowledge you have. In this part of Linux Interview Questions, we will discuss such questions.
You can use the cp command to copy a file in Linux. The general syntax is:
$ cp <source> <destination>
Suppose you want to copy a file named questions.txt from the directory /new/linux to /linux/interview, then the command will be:
$ cp questions.txt /new/linux /linux/interview
Every process has a unique process id. To terminate the process, we first need to find the process id. The ps command will list all the running processes along with the process id. And then we use the kill command to terminate the process.
The command for listing down all the processes:
$ ps
Suppose the process id of the process you want to terminate is 3849, then you will have to terminate it like this:
$ kill 3849
There is no specific command to rename a file in Linux. But you use the copy or move command to rename the file.
Using the Move command
$ mv <oldname> <newname>
Using the Copy command
$ cp <oldname> <newname>
And then delete the old file.
$ rm <oldname>
You can use the redirection operator (>) to do this.
Syntax: $ (command) > (filename)
By running the following command:
$ mount -l
You can use the locate command to find the path to the file.
Suppose you want to find the locations of a file name sample.txt, then your command would be:
$ locate sample.txt
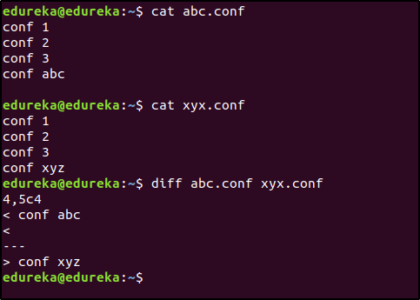
You can use the diff command for this:
$ diff abc.conf xyz.conf
for i in *linux*; do rm $i; done
The touch command can be used to create a text file without opening it. The touch command will create an empty file. The syntax is as follows:
$ touch <filename>
Suppose you want to create a file named sample.txt, then the command would be:
$ touch sample.txt
There are two commands that can be used to delete a directory in Linux.
$ rmdir <directory name>
$ rm -rf <directory name>
Note: The command rm -rf should be used carefully because it will delete all the data without any warnings.
There are two commands to schedule tasks in Linux: cron and at.
The cron command is used to repeatedly schedule a task at a specific time. The tasks are stored in a cron file and then executed using the cron command. The cron command reads the string from this file and schedules the task. The syntax for the string to enter in the cron file is as follows:
<minute> <hour> <day> <month> <weekday> <command>
Suppose you want to run a command at 4 pm every Sunday, then the string would be:
0 16 * * 0 <command>
The at command is used to schedule a task only once at the specified time.
Suppose you want to shut down the system at 6 pm today, then the command for this would be:
$ echo "shutdown now" | at -m 18:00
The .z extension means that the file has been compressed. To look at the contents of the compressed file, you can use the zcat command. Example:
$ zcat sample.z
Follow these steps to copy files to a Floppy Disk safely:
If you don’t unmount the floppy disk, then the data might become corrupted.
Open the terminal and run:
$ echo $SHELL
This will print the name of the Shell being used.
SSH can be used for this. The Syntax is as follows:
ssh <username>@<ip address>
Suppose you want to login into a system with IP address 192.168.5.5 as a user “mike”, then the command would be:
$ ssh [email protected]
$ vim -R <filename>
$ vim +/<employee id to be searched> <filename>
$ vim +<line number> <filename>
This can be done using the sort command.
$ sort sample.txt
The export command is used to set and reload the environment variables. For example, if you want to set the Java path, then the command would be:
$ export JAVA_HOME = /home/user/Java/bin
$ service <servicename> status
$ service --status-all
To start:
$ service <servicename> start
To stop:
$ service <servicename> start
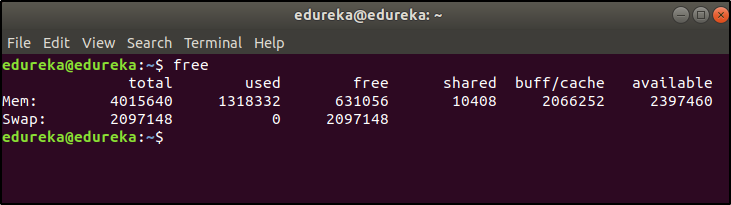
This command is used to display the free, used, swap memory available in the system.
Typical free command output. The output is displayed in bytes.
$ free
I hope these Linux Interview Questions will help you perform well in your interview. And I wish you all the best!
Got a question for us? Please post it on Edureka Community and we will get back to you.
If you wish to learn Linux Administration and build a colorful career, then check out our Linux Administration Training which comes with instructor-led live training and real-life project experience. This training will help you understand Linux Administration in depth and help you achieve mastery over the subject.
| Course Name | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| Linux Administration Certification Training Course | Class Starts on 18th February,2023 18th February SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
| Linux Administration Certification Training Course | Class Starts on 29th April,2023 29th April SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR  Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
edureka.co

l love this Q&A really very nice it is..,
Thank you, great Q&A for the interview. I’ve found a mistake where the command to stop a service is actually to start, just a note:
To stop:
$ service start———->should be “stop”
Thanks.