Full Stack Web Development Internship Program
- 5k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Today, Google and Facebook use JavaScript to build complex, desktop-like web applications. With the launch of Node.js, It has also become one of the most popular languages for building server-side software. Today, even the web isn’t big enough to contain JavaScript’s versatility. I believe that you are already aware of these facts and this has made you land on this JavaScript Interview Questions article.
So, if you are planning to start your career in JavaScript and you wish to know the skills related to it, now is the right time to dive in, when the technology is in its blossoming state. JavaScript Interview Questions and our JavaScript training and Java Certification training will provide you with in-depth knowledge and help you prepare for your interviews.
This Edureka video on “JavaScript Interview Questions” will help you to prepare yourself in advanced Java script concepts for you to clear the Java script interview on your first attempt.
The JavaScript interview questions are divided into three sections:
Let’s begin with the first section of JavaScript interview questions.
| Java | JavaScript |
| Java is an OOP programming language. | JavaScript is an OOP scripting language. |
| It creates applications that run in a virtual machine or browser. | The code is run on a browser only. |
| Java code needs to be compiled. | JavaScript code are all in the form of text. |
JavaScript is a lightweight, interpreted programming language with object-oriented capabilities that allows you to build interactivity into otherwise static HTML pages. The general-purpose core of the language has been embedded in Netscape, Internet Explorer, and other web browsers.
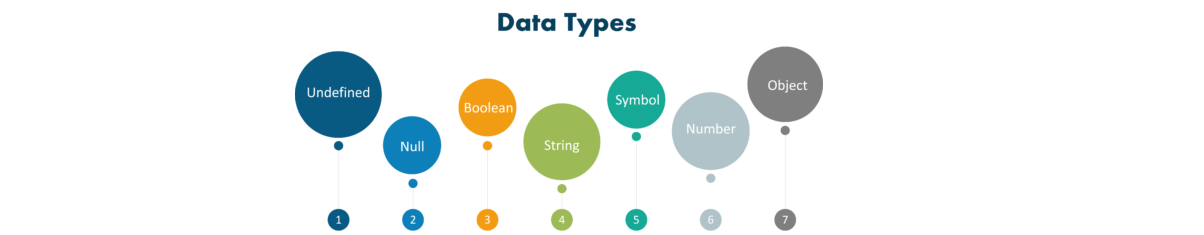
The data types supported by JavaScript are:

Following are the features of JavaScript:
Yes, JavaScript is a case sensitive language. The language keywords, variables, function names, and any other identifiers must always be typed with a consistent capitalization of letters.
 Following are the advantages of using JavaScript −
Following are the advantages of using JavaScript −
JavaScript supports Object concept very well. You can create an object using the object literal as follows −
var emp = {
name: "Daniel",
age: 23
};
You can define arrays using the array literal as follows-
var x = []; var y = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
A named function declares a name as soon as it is defined. It can be defined using function keyword as :
function named(){
// write code here
}
Yes! An anonymous function can be assigned to a variable. It can also be passed as an argument to another function.
In case you are facing any challenges with these JavaScript Interview Questions, please comment on your problems in the section below.
JavaScript variable arguments represents the arguments that are passed to a function. Using type of operator, we can get the type of arguments passed to a function. For example −
function func(x){
console.log(typeof x, arguments.length);
}
func(); //==> "undefined", 0
func(7); //==> "number", 1
func("1", "2", "3"); //==> "string", 3
The scope of a variable is the region of your program in which it is defined. JavaScript variable will have only two scopes.
• Global Variables − A global variable has global scope which means it is visible everywhere in your JavaScript code.
• Local Variables − A local variable will be visible only within a function where it is defined. Function parameters are always local to that function.
The JavaScript this keyword refers to the object it belongs to. This has different values depending on where it is used. In a method, this refers to the owner object and in a function, this refers to the global object.
A callback is a plain JavaScript function passed to some method as an argument or option. It is a function that is to be executed after another function has finished executing, hence the name ‘call back‘. In JavaScript, functions are objects. Because of this, functions can take functions as arguments, and can be returned by other functions.

Closures are created whenever a variable that is defined outside the current scope is accessed from within some inner scope. It gives you access to an outer function’s scope from an inner function. In JavaScript, closures are created every time a function is created. To use a closure, simply define a function inside another function and expose it.
| Built-in Method | Values |
| CharAt() | It returns the character at the specified index. |
| Concat() | It joins two or more strings. |
| forEach() | It calls a function for each element in the array. |
| indexOf() | It returns the index within the calling String object of the first occurrence of the specified value. |
| length() | It returns the length of the string. |
| pop() | It removes the last element from an array and returns that element. |
| push() | It adds one or more elements to the end of an array and returns the new length of the array. |
| reverse() | It reverses the order of the elements of an array. |
In case you are facing any challenges with these JavaScript Interview Questions, please comment on your problems in the section below.
The following rules are to be followed while naming variables in JavaScript:
The type of operator is used to get the data type of its operand. The operand can be either a literal or a data structure such as a variable, a function, or an object. It is a unary operator that is placed before its single operand, which can be of any type. Its value is a string indicating the data type of the operand.
The simplest way to create a cookie is to assign a string value to the document.cookie object, which looks like this-
Syntax :
document.cookie = "key1 = value1; key2 = value2; expires = date";
Reading a cookie is just as simple as writing one, because the value of the document.cookie object is the cookie. So you can use this string whenever you want to access the cookie.
If you want to delete a cookie so that subsequent attempts to read the cookie in JavaScript return nothing, you just need to set the expiration date to a time in the past. You should define the cookie path to ensure that you delete the right cookie. Some browsers will not let you delete a cookie if you don’t specify the path.
Now let’s move on to the next section of JavaScript interview questions.
Attributes- provide more details on an element like id, type, value etc.
Property- is the value assigned to the property like type=”text”, value=’Name’ etc.
Here are the list of ways an HTML element can be accessed in a Javascript code:
(i) getElementById(‘idname’): Gets an element by its ID name
(ii) getElementsByClass(‘classname’): Gets all the elements that have the given classname.
(iii) getElementsByTagName(‘tagname’): Gets all the elements that have the given tag name.
(iv) querySelector(): This function takes css style selector and returns the first selected element.
There are 3 different ways in which a JavaScript code can be involved in an HTML file:
An inline function is a JavaScript function, which is assigned to a variable created at runtime. You can differentiate between Inline Functions and Anonymous since an inline function is assigned to a variable and can be easily reused. When you need a JavaScript for a function, you can either have the script integrated in the page you are working on, or you can have it placed in a separate file that you call, when needed. This is the difference between an internal script and an external script.
The three possible ways of defining a variable in JavaScript are:
Typed Language is in which the values are associated with values and not with variables. It is of two types:

Local Storage – The data is not sent back to the server for every HTTP request (HTML, images, JavaScript, CSS, etc) – reducing the amount of traffic between client and server. It will stay until it is manually cleared through settings or program.
Session Storage – It is similar to local storage; the only difference is while data stored in local storage has no expiration time, data stored in session storage gets cleared when the page session ends. Session Storage will leave when the browser is closed.
In case you are facing any challenges with these JavaScript Interview Questions, please comment on your problems in the section below.
The main difference between “==” and “===” operator is that formerly compares variable by making type correction e.g. if you compare a number with a string with numeric literal, == allows that, but === doesn’t allow that, because it not only checks the value but also type of two variable, if two variables are not of the same type “===” return false, while “==” return true.
Undefined means a variable has been declared but has not yet been assigned a value. On the other hand, null is an assignment value. It can be assigned to a variable as a representation of no value. Also, undefined and null are two distinct types: undefined is a type itself (undefined) while null is an object.
Undeclared variables are those that do not exist in a program and are not declared. If the program tries to read the value of an undeclared variable, then a runtime error is encountered. Undefined variables are those that are declared in the program but have not been given any value. If the program tries to read the value of an undefined variable, an undefined value is returned.
 A JavaScript framework is an application framework written in JavaScript. It differs from a JavaScript library in its control flow. There are many JavaScript Frameworks available but some of the most commonly used frameworks are:
A JavaScript framework is an application framework written in JavaScript. It differs from a JavaScript library in its control flow. There are many JavaScript Frameworks available but some of the most commonly used frameworks are:
| Window | Document |
| JavaScript window is a global object which holds variables, functions, history, location. | The document also comes under the window and can be considered as the property of the window. |
innerHTML – It will process an HTML tag if found in a string
innerText – It will not process an HTML tag if found in a string
Event bubbling is a way of event propagation in the HTML DOM API, when an event occurs in an element inside another element, and both elements have registered a handle for that event. With bubbling, the event is first captured and handled by the innermost element and then propagated to outer elements. The execution starts from that event and goes to its parent element. Then the execution passes to its parent element and so on till the body element.
NaN is a short form of Not a Number. Since NaN always compares unequal to any number, including NaN, it is usually used to indicate an error condition for a function that should return a valid number. When a string or something else is being converted into a number and that cannot be done, then we get to see NaN.
In case you are facing any challenges with these JavaScript Interview Questions, please comment on your problems in the section below.
One of the differences between the two is that Primitive Data Types are passed By Value and Objects are passed By Reference.
The parseInt() function is used to convert numbers between different bases. It takes the string to be converted as its first parameter, and the second parameter is the base of the given string.
For example-
parseInt("4F", 16)
Since 2 and 5 are integers, they will be added numerically. And since 3 is a string, its concatenation will be done. So the result would be 73. The ” ” makes all the difference here and represents 3 as a string and not a number.
Imports and exports help us to write modular JavaScript code. Using Imports and exports we can split our code into multiple files. For example-
//------ lib.js ------</span>
export const sqrt = Math.sqrt;</span>
export function square(x) {</span>
return x * x;</span>
}
export function diag(x, y) {
return sqrt(square(x) + square(y));
}
//------ main.js ------</span>
{ square, diag } from 'lib';
console.log(square(5)); // 25
console.log(diag(4, 3)); // 5
Now with this, we have reached the final section of JS Interview Questions.
Strict mode is a way to introduce better error-checking into your code.
A prompt box is a box which allows the user to enter input by providing a text box. The prompt() method displays a dialog box that prompts the visitor for input. A prompt box is often used if you want the user to input a value before entering a page. When a prompt box pops up, the user will have to click either “OK” or “Cancel” to proceed after entering an input value.
var Y = 1;
if (function F(){})
{
y += Typeof F;</span>
}
console.log(y);
The output would be 1undefined. The if condition statement evaluates using eval, so eval(function f(){}) returns function f(){} (which is true). Therefore, inside the if statement, executing typeof f returns undefined because the if statement code executes at run time, and the statement inside the if condition is evaluated during run time.
The call() method calls a function with a given this value and arguments provided individually.
Syntax-
fun.call(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])
The apply() method calls a function with a given this value, and arguments provided as an array.
Syntax-
fun.apply(thisArg, [argsArray])
There are a number of methods you can use to empty an array:
Method 1 –
arrayList = []
Above code will set the variable arrayList to a new empty array. This is recommended if you don’t have references to the original array arrayList anywhere else, because it will actually create a new, empty array. You should be careful with this method of emptying the array, because if you have referenced this array from another variable, then the original reference array will remain unchanged.
Method 2 –
arrayList.length = 0;
The code above will clear the existing array by setting its length to 0. This way of emptying the array also updates all the reference variables that point to the original array. Therefore, this method is useful when you want to update all reference variables pointing to arrayList.
Method 3 –
arrayList.splice(0, arrayList.length);
The implementation above will also work perfectly. This way of emptying the array will also update all the references to the original array.
Method 4 –
while(arrayList.length)
{
arrayList.pop();
}
The implementation above can also empty arrays, but it is usually not recommended to use this method often.
var Output = (function(x)
{
Delete X;
return X;
}
)(0);
console.log(output);
The output would be 0. The delete operator is used to delete properties from an object. Here x is not an object but a local variable. delete operators don’t affect local variables.
In case you are facing any challenges with these JavaScript Interview Questions, please comment on your problems in the section below.
var X = { Foo : 1};
var Output = (function()
{
delete X.foo;
return X.foo;
}
)();
console.log(output);
The output would be undefined. The delete operator is used to delete the property of an object. Here, x is an object which has the property foo, and as it is a self-invoking function, we will delete the foo property from object x. After doing so, when we try to reference a deleted property foo, the result is undefined.
var Employee =
{
company: 'xyz'
}
var Emp1 = Object.create(employee);
delete Emp1.company Console.log(emp1.company);
The output would be xyz. Here, emp1 object has company as its prototype property. The delete operator doesn’t delete prototype property. emp1 object doesn’t have company as its own property. However, we can delete the company property directly from the Employee object using delete Employee.company.
//nfe (named function expression)
var Foo = Function Bar()
{
return 7;
};
typeof Bar();
The output would be Reference Error. A function definition can have only one reference variable as its function name.
This is an increasingly common practice, employed by many popular JavaScript libraries. This technique creates a closure around the entire contents of the file which, perhaps most importantly, creates a private namespace and thereby helps avoid potential name clashes between different JavaScript modules and libraries.
Another feature of this technique is to allow for an easy alias for a global variable. This is often used in jQuery plugins.
JavaScript escape characters enable you to write special characters without breaking your application. Escape characters (Backslash) is used when working with special characters like single quotes, double quotes, apostrophes and ampersands. Place backslash before the characters to make it display.
For example-
document.write "I am a "good" boy" document.write "I am a "good" boy"
With this, we have come to the end of the JavaScript interview questions blog. I Hope these JS Interview Questions will help you in your interviews. In case you have attended interviews in the recent past, do paste those interview questions in the comments section and we’ll answer them. You can also comment below if you have any questions in your mind, which you might face in your JavaScript interview.
If you wish to learn JavaScript and build your own applications, then check out our Web developer course online which comes with instructor-led live training and real-life project experience. Edureka’s Java training makes you proficient in skills to work with back-end and front-end web technologies. It includes training on Web Development, jQuery, Angular, NodeJS, ExpressJS and MongoDB.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of “JavaScript Interview Questions” blog and we will get back to you or you can also join our Java Training in Bangalore.

| Course Name | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| Java Certification Training Course | Class Starts on 28th January,2023 28th January SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
| Java Certification Training Course | Class Starts on 25th February,2023 25th February SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR  Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
edureka.co

Questions and answers are good but if there will be an example with code that it will be like awesome.
Very good article you publish helpful these question and answer are also important for java script learning students.
This post was really useful in terms of the information provided and the various level-wise questions. We have compiled the most important javascript interview topics list for anyone preparing for the Javascript interview.
Most of the questions are outdated and no longer asked in Interview.
Kindly hire a PROFESSIONAL and make articles.
Q41
First wi will see an Exception: SyntaxError: unexpected token: identifier
Because we must use tupeof not Typeof. When we fix that error we’ll see:
Exception: SyntaxError: expected expression, got ‘<' Because there is stray tag. When we fix that there goes:Exception: ReferenceError: y is not defined Because you declare var Y but use y. After we fix that bug we’ll see: 1undefinedYour questions are either careless or diabolically hard.Q45 Exception: SyntaxError: unexpected token: identifier Delete != delete Exception: SyntaxError: unexpected token: identifier X != x Exception: ReferenceError: output is not defined Output != output And after all these fixes we got 0 in console.Why do you care so little about code?Q46 Output != output X.Foo != X.fooQ47 Exception: SyntaxError: unexpected token: identifier Because there is missing ; Should be: delete Emp1.company; Exception: ReferenceError: employee is not defined Employee != employeeEmp1 != emp1Exception: ReferenceError: Console is not definedAnd after all these fixes we get xyzQ48 Exception: SyntaxError: unexpected token: identifier is it Function or function? Who knows… Fix that and no error. No output also. Needs console.log(typeof Bar()); And then output number… Why? Because this works. Function can have one name, but many aliases…Dude, it’s 2019! Why are you teaching people like this???