Full Stack Web Development Internship Program
- 5k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Are you thinking of pursuing your career in Spring Framework? Are you searching for an appropriate QnA set to prepare for your interviews? Here is a blog on Spring Interview Questions which discusses on top 50 questions with proper explanation and examples. It will definitely help you to ace the interviews. But before starting with the Spring Interview Questions, let’s take a quick look on Spring Framework’s demand and status in the market.
Since it’s release, the Spring Framework has continued to bloom in the market. Spring community is continuously coming up with new things and have spread into a vast ecosystem. Today, it holds the top position in the framework market. Check out the below graph which shows the frameworks most frequently used in the market as on January 2018.
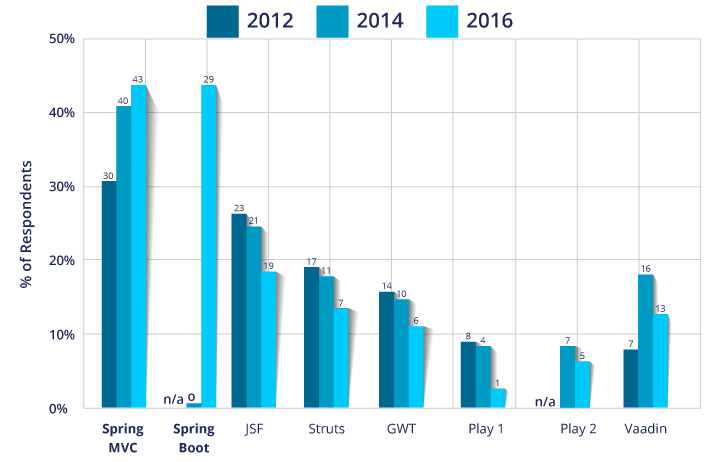
You might ask why is Spring certification so much in demand? Well, the answer is, because it provides a comprehensive programming and configuration model for modern Java-based enterprise applications. It is not concerned with the deployment platform used. A key element of Spring Framework is infrastructural support at the application level. It’s very much unlikely to go out of the market in the near future with more major releases announced.
Before we move any further let us take a look some of the most frequently asked Spring Interview Questions,
Q1. What are the major features in different versions of Spring Framework?
Q2. What is a Spring Framework?
Q3. List the advantages of Spring Framework
Q4. What are the different features of Spring Framework?
Q5. How many modules are there in Spring Framework and what are they?
Q6. What is a Spring configuration file?
Q7. What are the different components of a Spring application?
Q8. What are the various ways of using Spring Framework?
Q9. What is Spring IOC Container?
Q10. What do you mean by Dependency Injection?
So, here are the Top 50 Spring Interview Questions which are most likely to be asked by the interviewer. If you are seeking a future in this field, these questions will surely help you to ace the interview. For your ease of access, I have categorized the questions under a few topics, namely:
You may watch the webinar recording of Spring Interview Questions where our instructor has shared his experience and expertise that will help you to crack any Spring Interview.
Let’s begin with the first section of Spring interview questions that is the General Questions.
| Version | Logo | Feature |
| Spring 2.5 | This version was released in 2007. It was the first version which supported annotations. | |
| Spring 3.0 | This version was released in 2009. It made full-fledged use of improvements in Java5 and also provided support to JEE6. | |
| Spring 4.0 | This version was released in 2013. This was the first version to provide full support to Java 8. |
 Spring is a powerful open source, application framework created to reduce the complexity of enterprise application development.
Spring is a powerful open source, application framework created to reduce the complexity of enterprise application development. Following are some of the major features of Spring Framework :
There are around 20 modules which are generalized into Core Container, Data Access/Integration, Web, AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming), Instrumentation and Test.
Few Miscellaneous modules are given below:

A Spring configuration file is an XML file. This file mainly contains the classes information. It describes how those classes are configured as well as introduced to each other. The XML configuration files, however, are verbose and more clean. If it’s not planned and written correctly, it becomes very difficult to manage in big projects.
A Spring application, generally consists of following components:

Spring Framework can be used in various ways. They are listed as follows:
The next section of Spring Interview Questions is on Dependency Injection and IoC container.

At the core of the Spring Framework, lies the Spring container. The container creates the object, wires them together, configures them and manages their complete life cycle. The Spring container makes use of Dependency Injection to manage the components that make up an application. The container receives instructions for which objects to instantiate, configure, and assemble by reading the configuration metadata provided. This metadata can be provided either by XML, Java annotations or Java code.
In Dependency Injection, you do not have to create your objects but have to describe how they should be created. You don’t connect your components and services together in the code directly, but describe which services are needed by which components in the configuration file. The IoC container will wire them up together.
In general, dependency injection can be done in three ways, namely :
In Spring Framework, only constructor and setter injections are used.
| Constructor Injection | Setter Injection |
|---|---|
| There is no partial injection. | There can be partial injection. |
| It doesn’t override the setter property. | It overrides the constructor property. |
| It will create a new instance if any modification is done. | It will not create new instance if any modification is done. |
| It works better for many properties. | It works better for few properties. |
| BeanFactory | ApplicationContext |
|---|---|
| It is an interface defined in org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory | It is an interface defined in org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext |
| It uses Lazy initialization | It uses Eager/ Aggressive initialization |
| It explicitly provides a resource object using the syntax | It creates and manages resource objects on its own |
| It doesn’t supports internationalization | It supports internationalization |
| It doesn’t supports annotation based dependency | It supports annotation based dependency |
Some of the benefits of IoC are:
Let’s move on to the next section of Spring Interview Questions, that is Spring Beans Interview Questions.

Configuration metadata can be provided to Spring container in following ways:
<bean id="studentbean" class="org.edureka.firstSpring.StudentBean"> <property name="name" value="Edureka"></property> </bean>
<beans> <context:annotation-config/> <!-- bean definitions go here --> </beans>
@Configuration
public class StudentConfig
{
@Bean
public StudentBean myStudent()
{ return new StudentBean(); }
}
The Spring Framework supports five scopes. They are:
The last three are available only if the users use a web-aware ApplicationContext.
Bean life cycle in Spring Bean Factory Container is as follows:
To understand it in better way check the below diagram:

A bean can be declared as an inner bean only when it is used as a property of another bean. For defining a bean, the Spring’s XML based configuration metadata provides the use of <bean> element inside the <property> or <constructor-arg>. Inner beans are always anonymous and they are always scoped as prototypes. For example, let’s say we have one Student class having reference of Person class. Here we will be creating only one instance of Person class and use it inside Student.
Here’s a Student class followed by bean configuration file:
Student.java
public class Student
{
private Person person;
//Setters and Getters
}
public class Person
{
private String name;
private String address;
//Setters and Getters
}
studentbean.xml
<bean id=“StudentBean" class="com.edureka.Student"> <property name="person"> <!--This is inner bean --> <bean class="com.edureka.Person"> <property name="name" value=“Scott"></property> <property name="address" value=“Bangalore"></property> </bean> </property> </bean>
When beans are combined together within the Spring container, it’s called wiring or bean wiring. The Spring container needs to know what beans are needed and how the container should use dependency injection to tie the beans together, while wiring beans.

The Spring container is able to autowire relationships between the collaborating beans. That is, it is possible to let Spring resolve collaborators for your bean automatically by inspecting the contents of the BeanFactory.
Different modes of bean auto-wiring are:
Following are some of the limitations you might face with auto wiring:
In the next section, we will discuss on Spring Annotations Interview Questions.
Instead of using XML to describe a bean wiring, the developer moves the configuration into the component class itself by using annotations on the relevant class, method, or field declaration. It acts as an alternative to XML setups. For example:
@Configuration
public class AnnotationConfig
{
@Bean
public MyDemo myDemo()
{ return new MyDemoImpll(); }
}
By default, Annotation wiring is not turned on in the Spring container. Thus, to use annotation based wiring we must enable it in our Spring configuration file by configuring <context:annotation-config/> element. For example:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"> <context:annotation-config/> <beans ………… /> </beans>

@Component: This marks a java class as a bean. It is a generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component. The component-scanning mechanism of spring now can pick it up and pull it into the application context.
@Controller: This marks a class as a Spring Web MVC controller. Beans marked with it are automatically imported into the Dependency Injection container.
@Service: This annotation is a specialization of the component annotation. It doesn’t provide any additional behavior over the @Component annotation. You can use @Service over @Component in service-layer classes as it specifies intent in a better way.
@Repository: This annotation is a specialization of the @Component annotation with similar use and functionality. It provides additional benefits specifically for DAOs. It imports the DAOs into the DI container and makes the unchecked exceptions eligible for translation into Spring DataAccessException.
@Required is applied to bean property setter methods. This annotation simply indicates that the affected bean property must be populated at the configuration time with the help of an explicit property value in a bean definition or with autowiring. If the affected bean property has not been populated, the container will throw BeanInitializationException.
For example:
public class Employee
{
private String name;
@Required
public void setName(String name)
{this.name=name; }
public string getName()
{ return name; }
}
The @Autowired annotation provides more accurate control over where and how autowiring should be done. This annotation is used to autowire bean on the setter methods, constructor, a property or methods with arbitrary names or multiple arguments. By default, it is a type driven injection.
For Example:
public class Employee
{
private String name;
@Autowired
public void setName(String name)
{this.name=name; }
public string getName()
{ return name; }
}
When you create more than one bean of the same type and want to wire only one of them with a property you can use the @Qualifier annotation along with @Autowired to remove the ambiguity by specifying which exact bean should be wired.
For example, here we have two classes, Employee and EmpAccount respectively. In EmpAccount, using @Qualifier its specified that bean with id emp1 must be wired.
Employee.java
public class Employee
{
private String name;
@Autowired
public void setName(String name)
{ this.name=name; }
public string getName()
{ return name; }
}EmpAccount.java
public class EmpAccount
{
private Employee emp;
@Autowired
@Qualifier(emp1)
public void showName()
{
System.out.println(“Employee name : ”+emp.getName);
}
}
@RequestMapping annotation is used for mapping a particular HTTP request method to a specific class/ method in controller that will be handling the respective request. This annotation can be applied at both levels:
Next section of Spring Interview Questions is on Data Access.
The Data Access Object (DAO) support in Spring makes it easy to work with data access technologies like JDBC, Hibernate or JDO in a consistent way. This allows one to switch between the persistence technologies easily. It also allows you to code without worrying about catching exceptions that are specific to each of these technology.
See the below diagram, it depicts all the Spring DAO classes in the hierarchical order.

Classes present in JDBC API are as follows:
There are two ways by which we can access Hibernate using Spring:
Two types of transaction management are supported by Spring. They are:
Different ORM’s supported by Spring are depicted via the below diagram:
 The next section of Spring interview questions discusses on Spring AOP Interview Questions.
The next section of Spring interview questions discusses on Spring AOP Interview Questions.
Aspect-oriented programming or AOP is a programming technique which allows programmers to modularize crosscutting concerns or behavior that cuts across the typical divisions of responsibility. Examples of cross-cutting concerns can be logging and transaction management. The core of AOP is an aspect. It encapsulates behaviors that can affect multiple classes into reusable modules.
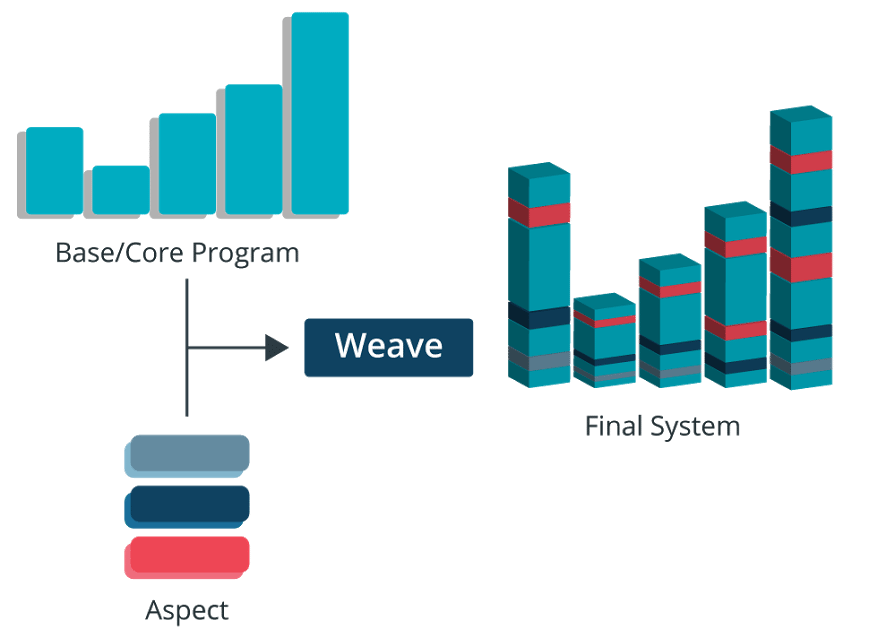
Aspect is a modularization of concern which cuts across multiple objects. Transaction management is a good example of a crosscutting concern in J2EE applications. Aspects are implemented using regular classes or regular classes annotated with the @Aspect annotation in Spring Framework.
A point during the execution of a program is called JoinPoint, such as the execution of a method or the handling of an exception. In Spring AOP, a joinpoint always represents a method execution.
An Action taken by an aspect at a particular joinpoint is known as an Advice. Spring AOP uses an advice as an interceptor, maintaining a chain of interceptors “around” the join point.
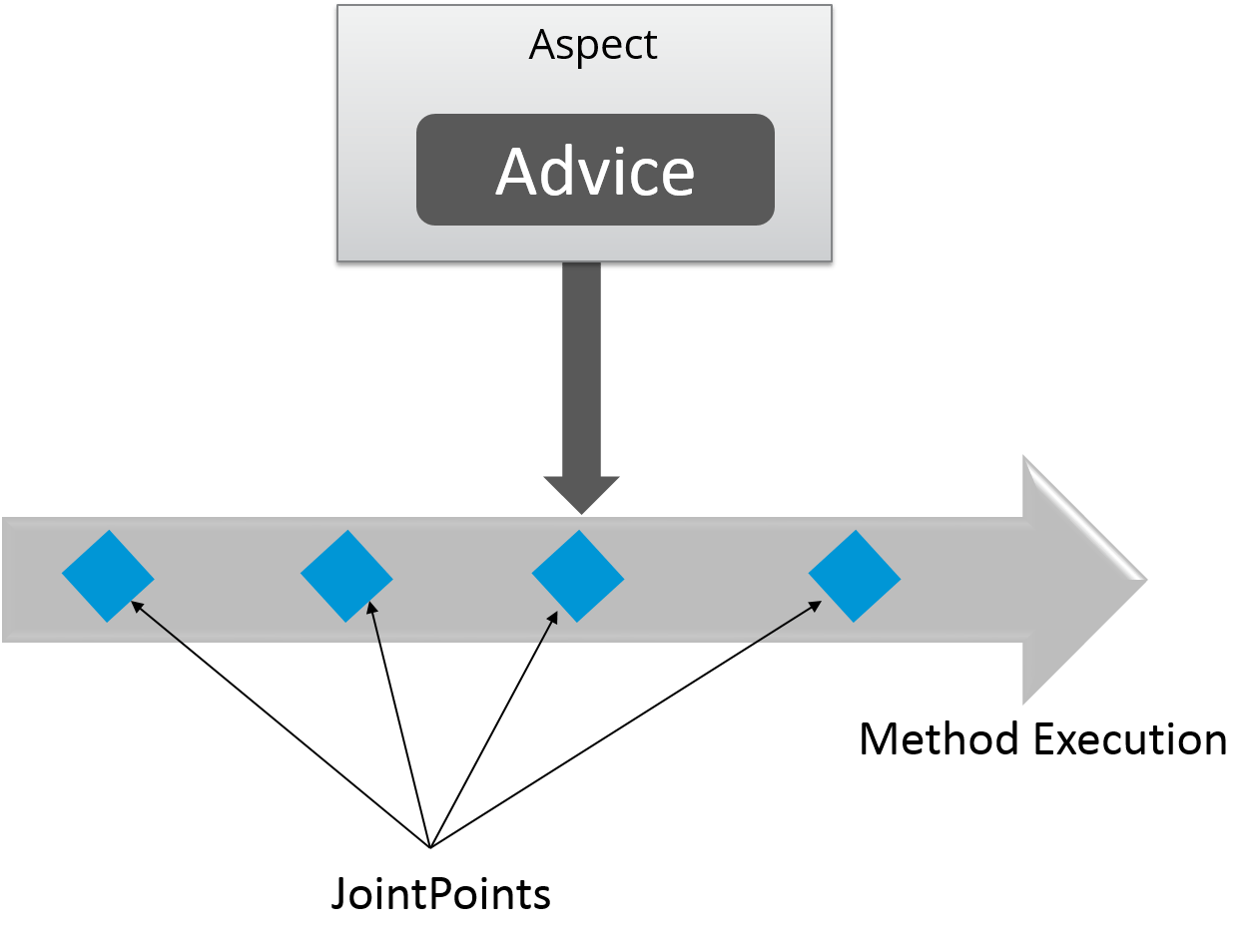
Different types of Advices in Spring AOP are:
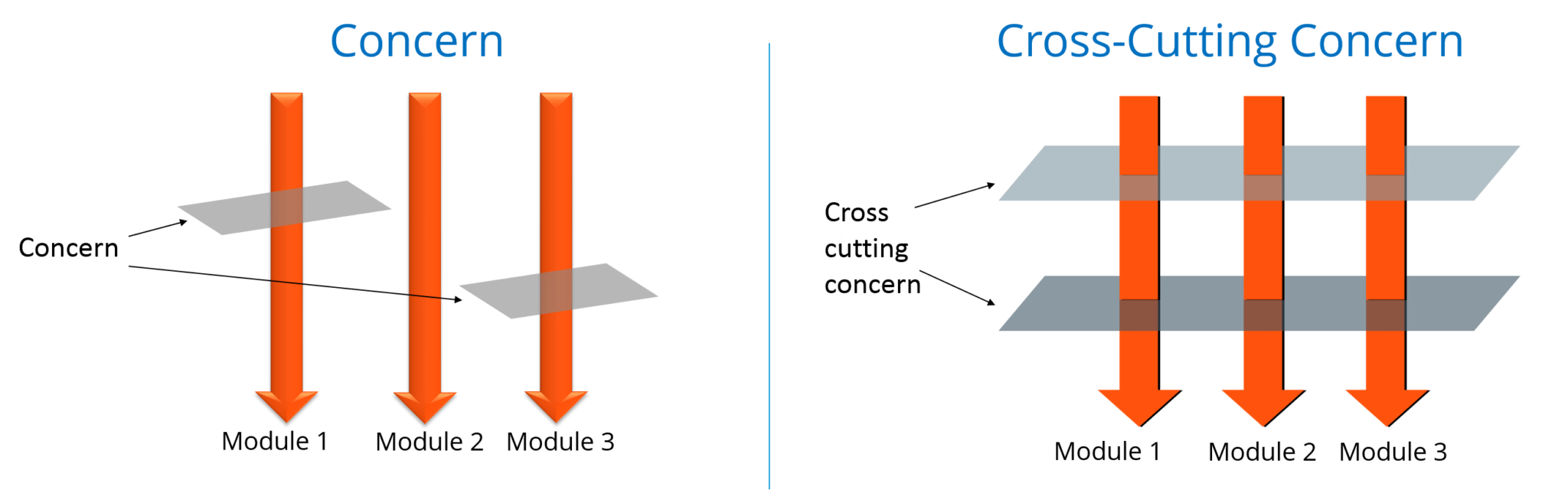
The concern is the behavior we want to have in a particular module of an application. It can be defined as a functionality we want to implement.
The cross-cutting concern is a concern which is applicable throughout the application. This affects the entire application. For example, logging, security and data transfer are the concerns needed in almost every module of an application, thus they are the cross-cutting concerns.
Different AOP implementations are depicted by the below diagram:

| Spring AOP | AspectJ AOP |
|---|---|
| Runtime weaving through proxy is done | Compile time weaving through AspectJ Java tools is done |
| It supports only method level PointCut | It suports field level Pointcuts |
| It is DTD based | It is schema based and Annotation configuration |
An object which is created after applying advice to a target object is known as a Proxy. In case of client objects the target object and the proxy object are the same.

The process of linking an aspect with other application types or objects to create an advised object is called Weaving. In Spring AOP, weaving is performed at runtime. Refer the below diagram:
 The last section of Spring interview questions is on Spring MVC Interview Questions.
The last section of Spring interview questions is on Spring MVC Interview Questions.
The Spring web MVC framework provides model-view-controller architecture and ready to use components that are used to develop flexible and loosely coupled web applications. The MVC pattern helps in separating the different aspects of the application like input logic, business logic and UI logic, while providing a loose coupling between all these elements. Get Started with Spring MVC
The DispatcherServlet is the core of Spring Web MVC framework. It handles all the HTTP requests and responses. The DispatcherServlet receives the entry of handler mapping from the configuration file and forwards the request to the controller. The controller then returns an object of Model And View. The DispatcherServlet checks the entry of view resolver in the configuration file and calls the specified view component.
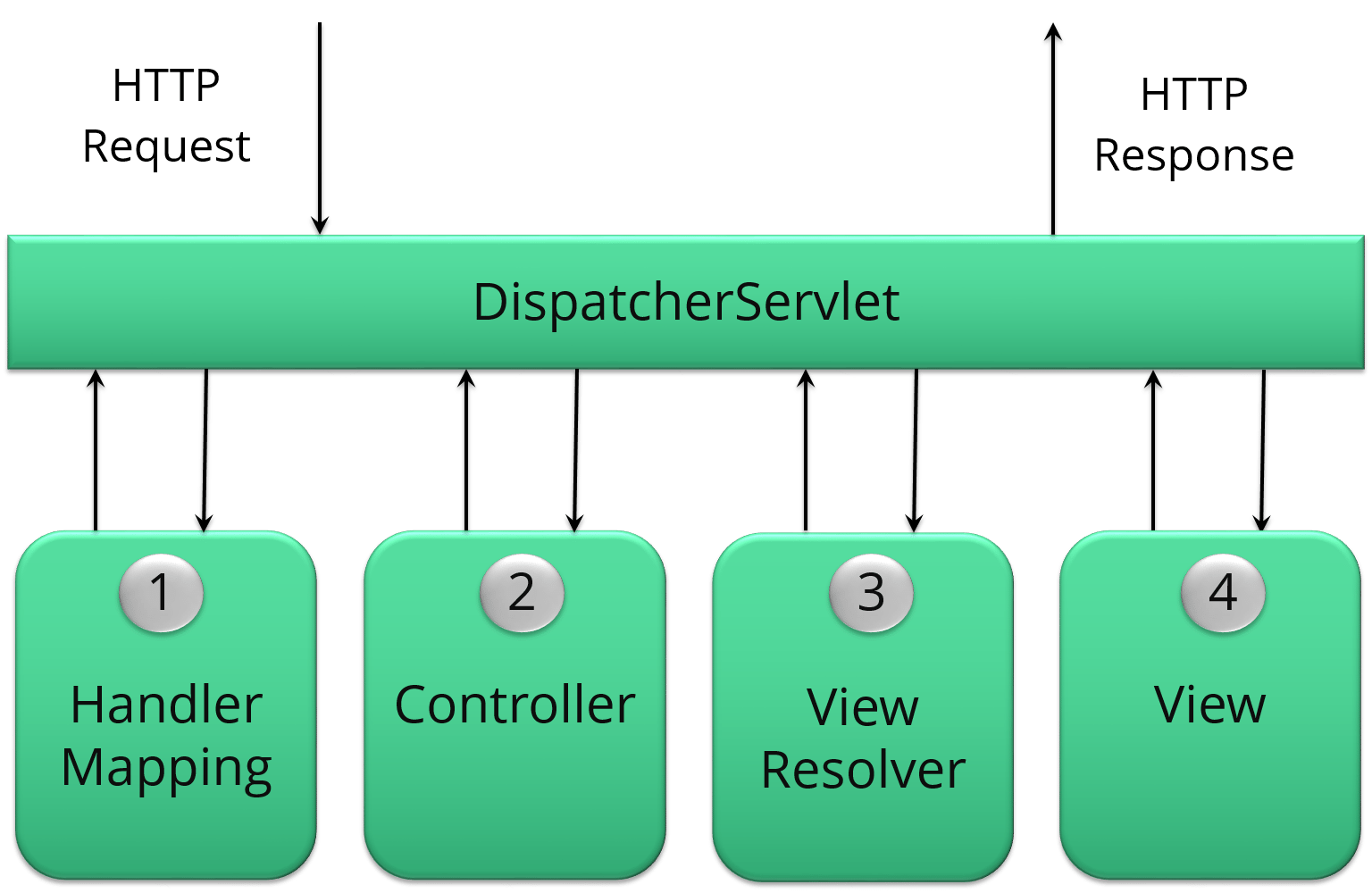
The WebApplicationContext is an extension of the plain ApplicationContext. It has some extra features that are necessary for web applications. It differs from a normal ApplicationContext in terms of its capability of resolving themes and in deciding which servlet it is associated with.
Controllers provide access to the application behavior. These behaviors are generally defined through a service interface. Controllers interpret the user input and transform it into a model which is represented to the user by the view. In Spring, controller is implemented in a very abstract way. It also enables you to create a wide variety of controllers.

I hope this set of Spring Interview Questions and Answers will help you in preparing for your interviews. All the best!
If you want to learn Spring and wish to use it while developing Java applications, then check out the Spring Certification Training by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section and we will get back to you.
| Course Name | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| Spring Framework Certification Course | Class Starts on 25th February,2023 25th February SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
| Spring Framework Certification Course | Class Starts on 22nd April,2023 22nd April SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR  Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
edureka.co

Thanks for nice article on spring interview questions
First ever seen the detailed covered topics. Thanks for supporting.
First ever seen such detailed topics covered. Thanks for supporting.
Good collection of all technical topics at one place !!
Awesome covered each and every topic
Hey Aman, thanks for the compliment. We are glad you loved the blog. Cheers!
Great Blog. You shared great topics with excellent content very clearly.
c++ interview questions
salesforce interview questions
bootstrap interview questions
spring interview questions and answers for experienced