Microsoft Power BI Certification Training Cou ...
- 47k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
In this Power BI Interview Questions blog, we will be discussing some of the most important interview questions associated with Power BI Certification which will help you stand out in your interview.
Power BI came into existence in late 2013 after Microsoft had decided to combine multiples excel add-ons to create a completely new and independent tool. Power BI has been the major contributing factor for Microsoft’s growth in the domain of Business Intelligence and Data Visualization in the year 2016-17. Below image is the change in positions of organizations in the Data Visualization domain as per Gartner:
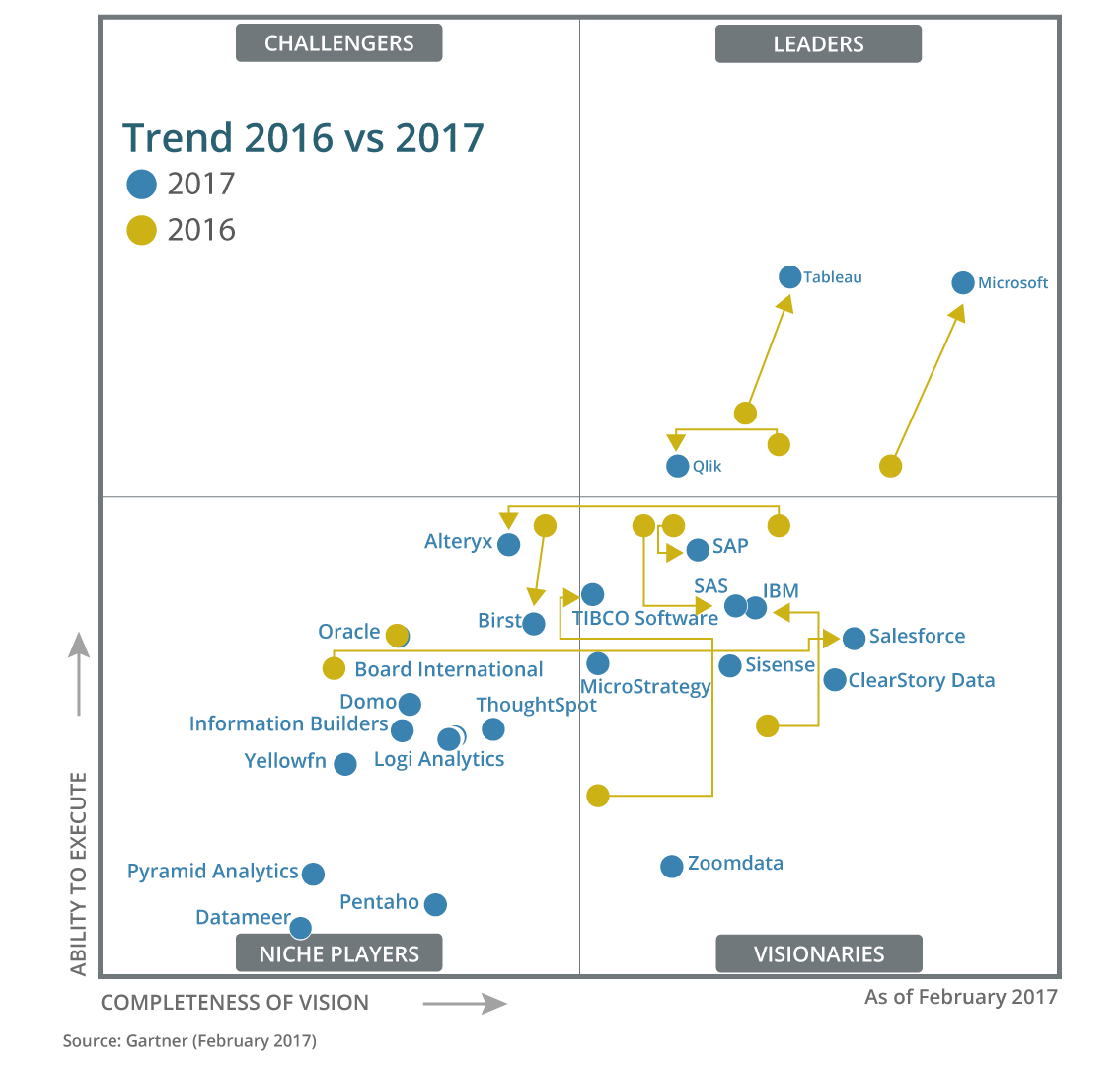
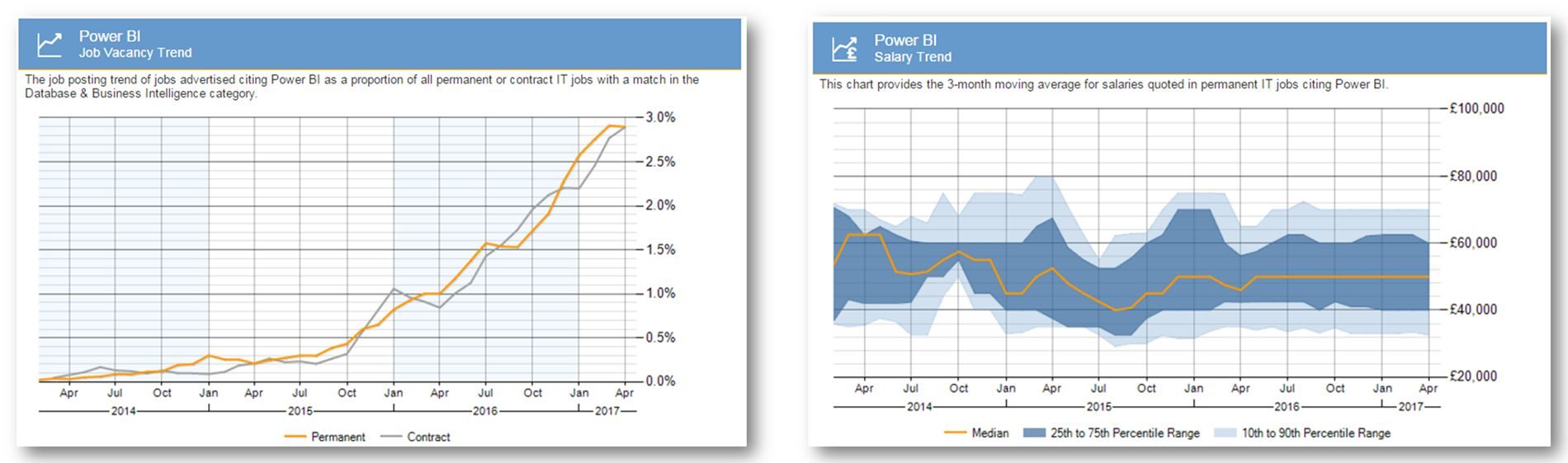
As you can see there is a major moment of Microsoft in the year 2017 when compared to 2016 and this is mainly due to the contribution oferal Power BI. In case you are still not convinced about moving into the Power BI domain, the below image will give you an idea about the current market for Power BI:
In this Power BI interview questions and answers blog, I have collected the most frequently asked questions by interviewers. These questions are collected after consulting with top industry experts in the field of Data analytics and visualization. If you want to brush up with the Power BI basics, you can take a look at this Power BI Tutorial blog. You can even get Power BI Training in Delhi or in any nearby city. Click below to know more.
So, here are the Top 50 Power BI Interview Questions and Answers which are most likely to be asked by the interviewer. For your ease of access, I have categorized the Power BI interview questions namely:
Power BI Interview Questions and Answers in 2023 | Edureka
This Edureka Power BI Interview Questions and Answers video will help you unravel concepts of Power BI and touch those topics that are very vital for succeeding in Power BI Interviews.
Ans: Microsoft has two parts for Self-Service BI
| Excel BI Toolkit | It allows users to create an interactive report by importing data from different sources and model data according to report requirement. |
| Power BI | It is the online solution that enables you to share the interactive reports and queries that you have created using the Excel BI Toolkit. |
Ans: Self-Service Business Intelligence (SSBI)

Ans: Power BI is a cloud-based data-sharing environment. Once you have developed reports using Power Query, Power Pivot, and Power View, you can share your insights with your colleagues. This is where Power BI enters the equation. Power BI, which technically is an aspect of SharePoint online, lets you load Excel workbooks into the cloud and share them with a chosen group of co-workers. Not only that, but your colleagues can interact with your reports to apply filters and slicers to highlight data. They are completed by Power BI, a simple way of sharing your analysis and insights from the Microsoft cloud.
Power BI features allow you to:
Ans: PowerBI is a cloud based Business Intelligence tool to analyze and visualize raw data that can be fetched from a wide range of data sources. It consolidates business analytics with data visualization and helps any organization to make business decisions based on data.It is easy to work with and the data is processed in such a way that it is easy to understand and reliable. It can be accessed from different platforms and can be shared across on-cloud participants. Thus it is an effective solution.
Ans: The major components of PowerBI are as follows :
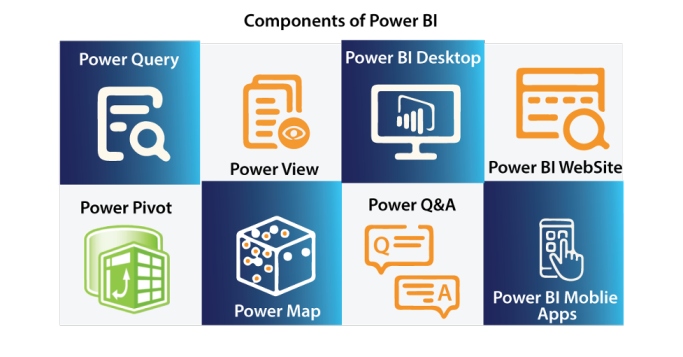
Let’s discuss each component in brief:
Power Query: It is one of the most important components of PowerBI to transform data. Power Query helps to extract data from different data sources like Oracle, SQL, Text/CSV files, Excel, etc. and even delete data from different sources.
Power Pivot : It is used for data modeling that uses DAX ( Data Analysis Expression) functions for the calculations. Relationships between different tables can also be created here and we can get values that can be shown in Pivot Tables.
Power View: The Power View is used for providing an intuitive display of the data and retrieving the metadata for data analysis. The views are interactive in nature and slicers and filters can be used for slicing and dicing the data.
Power BI Desktop: Power Desktop is an integration tool for Power Query, Power View, and Power Pivot. It helps to create advanced queries, data models, reports and dashboards and helps in developing your BI skills for data analysis.
Power BI Mobile Application: It is available for the Operating systems Android, iOS and even Windows. The App has an interactive display of the dashboards which can be shared as well.
Power Map: It presents geo-spatial visualization of the data in 3 Dimensional Mode. The data can be highlighted based on the geographical location which can be continent, state, city or even street address.
Power Q&A : It is used to provide answers to the questions asked by users. It works with Power View and can be answered with representations by Power Q&A.
Ans: PowerBI has three versions currently:
Microsoft PowerBI Free/ Desktop – It is for anybody who wants to see their business insights from the data with visualizations.
Microsoft PowerBI Pro – It is the full version of PowerBI which enables unlimited viewing, reporting and sharing of reports which PowerBI Desktop doesn’t support.
Microsoft PowerBI Premium – The Power BI Premium licence is not a per-user licence, it provides a dedicated unit of capacity for all users in the organisation.
Ans: Power BI Desktop is a free desktop application that can be installed right on your own computer. Power BI Desktop works cohesively with the Power BI service by providing advanced data exploration, shaping, modeling, and creating reports with highly interactive visualizations. You can save your work to a file or publish your data and reports right to your Power BI site to share with others.
Ans: PowerBI Services is a cloud based service or SaaS (software as a service). It helps to connect to your data, analyse, visualize and share business insights with efficiency.
Ans: The list of data sources for Power BI is extensive, but it can be grouped into the following:
Ans: There are three different connectivity modes in PowerBI which are:
Import Mode:
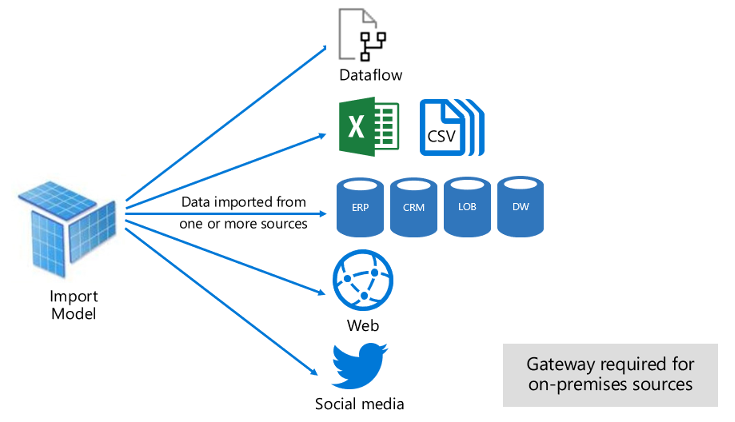
In PowerBI, Import Mode is the default mode since it is most frequently used and delivers fast performance. It can integrate the data from a data source as shown. Imported data is stored in the disk and it is fully loaded while querying or refreshing.
Direct Query Mode
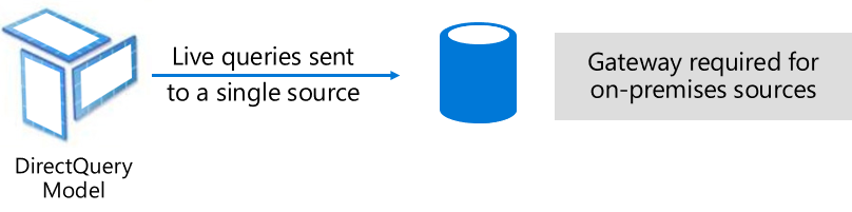
Direct Query Mode is another method of importing data with query to retrieve data from a pre-existing data source. When the data volume is too large, we use DirectQuery to avoid refreshing data as it can take a long time.
Composite Mode
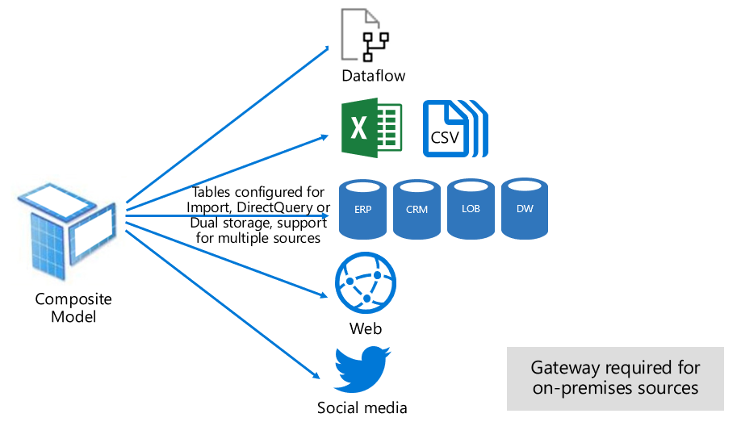
This mode is an amalgamation of both Import and DirectQuery modes. This mode supports calculated tables which DirectQuery doesn’t. It delivers the best of Import Query and DirectQuery modes.
Ans: Primarily, PowerBI uses two repositories to store its data: Azure Blob Storage and Azure SQL Database. Azure Blob Storage typically stores the data that is uploaded by the users. Azure SQL Database stores all the metadata and artifacts for the system itself.
Ans: The following are the Building Blocks (or) key components of Power BI:
Ans. Power BI’s working system mainly comprises four steps:
Data Importing: The first step is to import the data and convert it into a standard format and store it in a staging area.
Data Cleaning: After assembling the data, it requires transformation or cleaning to remove unimportant values.
Data Visualization: Now the data is visually represented on the Power BI desktop as reports and dashboards using powerful visualization tools.
Save and Publish: Finally when your report is ready you can save and publish these reports that can be shared across users via mobile apps or web.
Ans: Content packs for services are pre-built solutions for popular services as part of the Power BI experience. A subscriber to a supported service, can quickly connect to their account from Power BI to see their data through live dashboards and interactive reports that have been pre-built for them. Microsoft has released content packs for popular services such as Salesforce.com, Marketo, Adobe Analytics, Azure Mobile Engagement, CircuitID, comScore Digital Analytix, Quickbooks Online, SQL Sentry and tyGraph.
Organizational content packs provide users, BI professionals, and system integrator the tools to build their own content packs to share purpose-built dashboards, reports, and datasets within their organization.
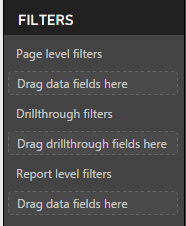 Ans: Power BI provides variety of option to filter report, data and visualization. The following are the list of Filter types.
Ans: Power BI provides variety of option to filter report, data and visualization. The following are the list of Filter types.
We know that Power BI visual has an interactions feature, which makes filtering a report a breeze. Visual interactions are useful, but they come with some limitations:
Ans: A PowerBI dashboard is a canvas which creates a story with templates and visualizations for better understanding of the data. It is a single-page report and contains the highlights of the data.
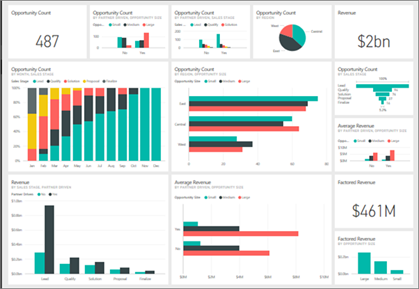
Ans: The different views in PowerBI are:
Report View : It is the default view which shows the visualization of the data in reports. You can create multiple report pages here with a wide range of templates and visualizations.
Data View : Data view shows the transformed data in a table format with columns and rows. It also allows you to create new calculated columns for further insights.
Model View : Also called, Relationship View, helps to create relationships between data models. All the models created in the data can be seen in this view and accordingly you can compare or create diagrams based on subsets of the model.
Ans: Power BI is available in different formats:
Power BI desktop: You can download and install PowerBI Desktop on your personal computer, where you can connect to the data source, transform your data, analyze and visualize it with templates.
Power BI services: It is a cloud based service or SaaS (software as a service). You can connect to data here as well but the modeling is limited.
Power BI mobile app: One can securely access dashboards and reports on any device with the PowerBI app which is available for iOs, Android and even Windows.
Ans: In PowerBI, we can represent the data in graphs and visualizations. The visualization can be of any type, for example:
Bar and Column Charts: It is a standard visualization for looking at a specific value across various categories.
Area Charts( Basic and Stacked ) : It is based on the line chart and the area under the line. It depicts the magnitude of change over time.
Card: Card shows aggregate value of a certain datapoint, can be one or more but one per row.
Doughnut and Pie Charts: They show the relation in parts of a whole. Doughnut charts have a hollow in the centre while pie charts don’t.
Maps: To show categorical and quantitative data with spatial locations.
Matrix: It’s a type of table with easier display that shows aggregated data
Slicers: Slicer is used to filter other visuals on the page.
There are other visuals like Combo Charts, Decomposition Tree, Funnel charts, Gauge charts, KPIs, Line Charts, Ribbon Chart, Scatter, Q&A, Tables, Treemaps, etc.
Ans: In PowerBI you can create your own visualizations from the library of custom visualizations. A development project has to be created then test the visual in PowerBI service. Once the visualization is customized, it is thoroughly checked and tested before posting. After testing, the visualization is saved in .pbiviz file format before sharing. But you need to be a PowerBI Pro user in order to make custom visualizations.
Ans: A custom visual file is used when none of the pre existing visuals fit the business needs. Custom visual files are generally created by Developers which can be used in the same way as prepackaged files.
Ans: PowerBI can be used by anyone for their requirements but there is a particular group of users who are more likely to use it:
Report Consumers: They consume the reports based on a specific information they need
Report Analyst: Report Analysts need detailed data for their analysis from the reports
Self Service Data Analyst: They are more experienced business data users. They have an in-depth understanding of the data to work with.
Basic Data Analyst: They can build their own datasets and are experienced in PowerBI Service
Advanced Data Analyst: They know how to write SQL Queries and have hands-on experience on PowerBI. They have experience in Advanced PowerBI with DAX training and data modelling.
Ans: The most important components of PowerBI are:
Power Query
Power View
Power Pivot
Power Map
Power Q&A
Power Desktop
Power Website
PowerBI Mobile App
Ans: With a Power BI Free licence a user can use 10 GB of storage in the cloud for hosting Power BI reports. The maximum size a Power BI report can be used in the cloud is 1GB.
Ans: The data can be reshaped in Data Editing of PowerBI.
Ans: The data can be refreshed in the Gateway in PowerBI by scheduling refresh.
Ans: PowerBI service dashboard is a single-page canvas that uses visualizations to depict a story.
Ans: Few advantages of using Power BI are :
Ans: Some disadvantages of PowerBI are:
Complex in nature:
One major drawback of PowerBI is it is designed in a complex manner. One needs complete knowledge of PowerBI in order to start working with PowerBI.
Large data:
PowerBI cannot handle large supply of data and might time out while processing a large data.
PowerBI cannot process data more than 1 GB.
Limited Sharing of Data:
Reports can be shared only with users who have the same domain or have their emails listed in the Office 365.
Limited data Source:
Power BI can connect to real time data sets but there are very limited data sources that allow real-time connection to the PowerBI dashboards.
Ans: To do basic calculation and data analysis on data in power pivot, we use Data Analysis Expression (DAX). It is a formula language used to compute calculated column and calculated field.
Sample DAX formula syntax:
For the measure named Total Sales, calculate (=) the SUM of values in the [SalesAmount] column in the Sales table.

A- Measure Name
B- = – indicate beginning of formula
C- DAX Function
D- Parenthesis for Sum Function
E- Referenced Table
F- Referenced column name
Ans: Below are some of the most commonly used DAX function:
Ans: Three fundamental concepts of DAX are:
Syntax: Syntax is the formula which includes the functions. If a Syntax is incorrect, it will result in an error.
Functions: Functions are arguments with specific orders to perform. It helps to calculate any particular order as required.
Context: Context are of two types: Row Context and Filter Context. Row Context is used when a formula has a Function that applies a filter to identify a row in a table. Filter Context is used when one or more filters are used to get a value.
Ans: DAX or Data Analysis Expression is a functional language which can create calculated columns and/or measures for smarter calculations to limit the data the dashboard has to fetch and visualize.
Ans: The FILTER function returns a table with a filter condition applied for each of its source table rows. The FILTER function is rarely used in isolation, it’s generally used as a parameter to other functions such as CALCULATE.
Ans: The CALCULATE function measures the sum of a column from any table and can be modified with Filters.
Syntax:
CALCULATE ( <Expression> [, <Filter> [, <Filter> [, … ] ] ] )
Expression: The expression to be evaluated.
Filter: A boolean (True/False) expression or a table expression that defines a filter.
Ans: These are the only functions that allow you modify filter context of measures or tables.
Limitations:
Ans: SUMMARIZE()
SUMMARIZECOLUMNS
Ans: DAX or Data Analysis Expression is a functional language which can create calculated columns and/or measures for smarter calculations to limit the data the dashboard has to fetch and visualise.
Ans: The solution will involve:
Alternatively, CONTAINS may be used:
Ans: Below are the most important BI add-in to Excel:
Ans: Power Pivot is an add-in for Microsoft Excel 2010 that enables you to import millions of rows of data from multiple data sources into a single Excel workbook. It lets you create relationships between heterogeneous data, create calculated columns and measures using formulas, build PivotTables and PivotCharts. You can then further analyze the data so that you can make timely business decisions without requiring IT assistance.
Ans: It is a model that is made up of data types, tables, columns, and table relations. These data tables are typically constructed for holding data for a business entity.
Ans: The main engine behind power pivot is the xVelocity in-memory analytics engine. It can handle large amount of data because it stores data in columnar databases, and in memory analytics which results in faster processing of data as it loads all data to RAM memory.
Ans: Here are some of the differences:
Ans: No, we cannot have more than one active relationship between two tables. However, can have more than one relationship between two tables but there will be only one active relationship and many inactive relationships. The dotted lines are inactive and the continuous line is active.
Find out our Power BI Training Course in Top Cities
With “Get Data” in PowerBI, you connect to different data sources to import data for analysis and visualization. You can select from a range of various data sources to import the desired data.
Eg. Text/CSV, Excel, PDF, JSON, Amazon Redshift, SQL Server database, Access database, SAP HANA database, IBM, MySQL, Oracle database, Impala, Google BigQuery,etc.
Ans: Power query is a ETL Tool used to shape, clean and transform data using intuitive interfaces without having to use coding. It helps the user to:
Ans: There are two destinations for output we get from power query:
Ans: Query folding is when steps defined in Power Query/Query Editor are translated into SQL and executed by the source database rather than the client machine. It’s important for processing performance and scalability, given limited resources on the client machine.
Ans: Changing Data Types, Filtering Rows, Choosing/Removing Columns, Grouping, Splitting a column into multiple columns, Adding new Columns ,etc.
Ans: Yes, a SQL statement can be defined as the source of a Power Query/M function for additional processing/logic. This would be a good practice to ensure that an efficient database query is passed to the source and avoid unnecessary processing and complexity
by the client machine and M function.
Ans:Query parameters can be used to provide users of a local Power BI Desktop report with a prompt, to specify the values they’re interested in.
Parameters and templates can make it possible to share/email smaller template files and limit the amount of data loaded into the local PBIX files, improving processing time and experience.
Ans: A new programming language is used in power query called M-Code. It is easy to use and similar to other languages. M-code is case-sensitive language.
Ans: Power Query is a self-service ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool which runs as an Excel add-in. It allows users to pull data from various sources, manipulate said data into a form that suits their needs and load it into Excel. It is most optimum to use Power Query over Power Pivot as it lets you not only load the data but also manipulate it as per the users needs while loading.
Ans: Some commonly used tasks in the Query Editor are:
Connect to Data: Get Data from various sources and Transform data.
Shape Data: Transform your data according to requirement to clean and shape it
Group Rows: You can group the values of many rows into one single value by summarizing
Pivot Columns: Pivot columns and create a table with aggregated values
Create Custom Columns: You can use custom formulas to create new columns in your table
Advanced Editor: You can make modifications to the data using Advanced Query Editor with query.
Ans: Power Map is an Excel add-in that provides you with a powerful set of tools to help you visualize and gain insight into large sets of data that have a geo-coded component. It can help you produce 3D visualizations by plotting upto a million data points in the form of column, heat, and bubble maps on top of a Bing map. If the data is time stamped, it can also produce interactive views that display, how the data changes over space and time.
Ans: For a data to be consumed in power map there should be location data like:
The primary requirement for the table is that it contains unique rows. It must also contain location data, which can be in the form of a Latitude/Longitude pair, although this is not a requirement. You can use address fields instead, such as Street, City, Country/Region, Zip Code/Postal Code, and State/Province, which can be geolocated by Bing.
Ans: The data can either be present in Excel or could be present externally. To prepare your data, make sure all of the data is in Excel table format, where each row represents a unique record. Your column headings or row headings should contain text instead of actual data so that Power Map will interpret it correctly when it plots the geographic coordinates. Using meaningful labels also makes value and category fields available to you when you design your tour in the Power Map Tour Editor pane.
To use a table structure that more accurately represents time and geography inside Power Map includes all of the data in the table rows, and use descriptive text labels in the column headings, like this:
In case you wish to load your data from an external source:
The more you use it, the better you’ll get at it. So, let’s get started.
Ans: Both PowerBi and Tableau are business intelligence tools for generating reports and data visualization but they do have a few significant differences.
Data Source:
PowerBI does not have as wide access to data sources as Tableau when compared. Tableau has a wider range of access to various data sources.
Data Capacity:
Maximum of 10 GB of data can be handled in each workspace in PowerBI or else it needs to be stored in the cloud.
While in Tableau, we can fetch billions of rows for each column as it works on columnar based structure which stores unique values.
Machine Learning:
PowerBI has integration with Microsoft Azure which helps in analyzing the data.
Tableau has in-built Python machine learning capacities which makes it efficient to perform ML Operations on datasets.
Performance:
PowerBI can handle a limited amount of data while Tableau can work with a huge volume of data with ease.
Pricing:
PowerBI is cheaper compared to Tableau. Tableau needs to be paid more when third party applications are connected.
Ans: Power View is a data visualization technology that lets you create interactive charts, graphs, maps, and other visuals which bring your data to life. Power View is available in Excel, SharePoint, SQL Server, and Power BI.
The following pages provide details about different visualizations available in Power View:
Ans: It is a stand alone application where we can make Power BI reports and then upload it to Powerbi.com, it does not require Excel. Actually, it is a combination of Power Query, Power Pivot, and Power View.
Ans: Yes we can refresh our reports through Data Management gateway(for sharepoint), and Power BI Personal gateway(for Powerbi.com)
Ans: There are four main types of refresh in Power BI. Package refresh, model or data refresh, tile refresh and visual container refresh.
This synchronizes your Power BI Desktop, or Excel, file between the Power BI service and OneDrive, or SharePoint Online. However, this does not pull data from the original data source. The dataset in Power BI will only be updated with what is in the file within OneDrive, or SharePoint Online.
It refers to refreshing the dataset, within the Power BI service, with data from the original data source. This is done by either using scheduled refresh or refresh now. This requires a gateway for on-premises data sources.
Tile refresh updates the cache for tile visuals, on the dashboard, once data changes. This happens about every fifteen minutes. You can also force a tile refresh by selecting the ellipsis (…) in the upper right of a dashboard and selecting Refresh dashboard tiles.
Refreshing the visual container updates the cached report visuals, within a report, once the data changes.
To know more about data refresh and understand how to implement data refresh, you can check the following link.
Ans: No, Power BI is not available as a private, internal cloud service. However, with Power BI and Power BI Desktop, you can securely connect to your own on-premises data sources. With the On-premises Data Gateway, you can connect live to your on-premises SQL Server Analysis Services and other data sources. You can also schedule refresh with a centralized gateway. If a gateway is not available, you can refresh data from on-premises data sources using the Power BI Gateway – Personal.
Ans: Gateway acts a bridge between on-premises data sources and Azure cloud services.
Ans: Power BI Q&A is a natural language tool that helps in querying your data and getting the results you need from it. You do this by typing into a dialog box on your Dashboard, which the engine instantaneously generates an answer similar to Power View. Q&A interprets your questions and shows you a restated query of what it is looking from your data. Q&A was developed by Server and Tools, Microsoft Research, and the Bing teams to give you a complete feeling of truly exploring your data.
Ans: When you click the Infocus mode of a tile on the PowerBI dashboard on the browser, the selected tile expands and takes the full space
Ans: Join Queries are used to consolidate inquiries in Power BI.
Ans: Below are some of the ways through which we can leverage Power BI:
Ans: Calculated Columns are DAX expressions that are computed during the model’s processing/refresh process for each row of the given column and can be used like any other column in the model.
Calculated columns are not compressed and thus consume more memory and result in reduced query performance. They can also reduce processing/refresh performance if applied on large fact tables and can make a model more difficult to maintain/support given
that the calculated column is not present in the source system.
Ans: Power BI can apply Row Level Security roles to models.
Ans: Many to Many relationships involve a bridge or junction table reflecting the combinations of two dimensions (e.g. doctors and patients). Either all possible combinations or those combinations that have occurred.
Ans: There are mainly 2 reasons why we would have tables without relations in our model:
Ans: You can use Power BI publisher for Excel to pin ranges, pivot tables and charts to Power BI.
The Publisher installs all necessary drivers on local machine to establish connectivity .
Ans: Dataset: The source used to create reports and visuals/tiles.
Report: An individual Power BI Desktop file (PBIX) containing one or more report pages.
Dashboard: a collection of visuals or tiles from different reports and, optionally, a pinned.
Ans: The 3 edit interaction options are Filter, Highlight, and None.
Filter: It completely filter a visual/tile based on the filter selection of another visual/tile.
Highlight: It highlight only the related elements on the visual/tile, gray out the non-related items.
None: It ignore the filter selection from another tile/visual.
Ans: With a data model local to the PBIX file (or Power Pivot workbook), the author has full control over the queries, the modeling/relationships, the metadata and the metrics.
With a live connection to an Analysis Services database (cube) the user cannot create new metrics, import new data, change the formatting of the metrics, etc – the user can only use the visualization, analytics, and formatting available on the report canvas.
With a direct query model in Power BI to SQL Server, for example, the author has access to the same features (and limitations) available to SSAS Direct Query mode.
Ans: Below are some of the way through which SSRS can be integrated with Power BI:
I hope this set of Power BI Interview Questions and Answers will help you prepare for your interviews. All the best!
Also, If you wish to build a career in business intelligence, our Business Intelligence Course will help you mine that data and enhance the decision-making processes throughout your organization.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section and we will get back to you
| Course Name | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Power BI Certification Training Course | Class Starts on 28th January,2023 28th January SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
| Microsoft Power BI Certification Training Course | Class Starts on 30th January,2023 30th January MON-FRI (Weekday Batch) | View Details |
| Microsoft Power BI Certification Training Course | Class Starts on 25th February,2023 25th February SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR  Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
edureka.co

Very very useful definations and thank to you all who are gathered this much of simple language.. all are can easily understand..
Q41. Which of the following statements create a dictionary?
Answer: b, c & d.
What??? d = {} creates a dictionary. Albeit an empty one. type(d) returns class ‘dict’ (or type ‘dict’ in Python2) as I expected it to. Answer d ( d = (40:”john”,45:”50″) ) throws a SyntaxError, again as I expected (even if I fix the double-quotes), in both Python2 and Python3. That’s definitely not how you make a dictionary. I don’t know what’s going on with the double quotes. I’d assume they were auto-inserted by a word processor, except that c and d both start and end with double right quotes. Are they just there to deliberately try to confuse people? Either way, they are not valid Python syntax. The only one the article says is not the correct answer is actually the only correct answer. It’s the only one that doesn’t throw a SyntaxError, let alone creates a dictionary. Assuming it’s a typographical error and all the quotes are meant to be normal double quotes, the correct answer is a, b, & c.
erratum in 25) Please change to
display = () => {
const name = this.inputDemo.value;
document.getElementById(“disp”).innerHTML = name;
};
Hi Swatee. Nice write-up. One question: why do you keep saying react is server rendered? It offers SSR, but in most of the SPA, it’s rendered at the browser, isn’t it?