Full Stack Web Development Internship Program
- 5k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
In this MVC interview questions article, I have collected the most frequently asked questions which are collected after consulting with top industry experts in the field of design patterns, ASP.NET and Spring Framework. If you want to brush up with the MVC basics, which I recommend you to do before going ahead with this MVC Interview Questions, take a look at this article on MVC Architecture.
In case you came across some other questions during your interviews or have queries that might be helpful for others as well, do share them in the comment section. This MVC Interview question is divided into the following sections:
Let’s begin this MVC interview questions with beginners level questions first.
Beginners Level MVC Interview Questions
| Components | Description |
Model | It represents the application data domain. In other words, applications business logic is contained within the model and is responsible for maintaining data. |
View | It represents the user interface, with which the end-users communicates. In short, all the user interface logic is contained within the VIEW. |
Controller | It is the controller that answers to user actions. Based on the user actions, the respective controller responds within the model and choose a view to render that display the user interface. The user input logic is contained with-in the controller. |
Below figure represents the same.
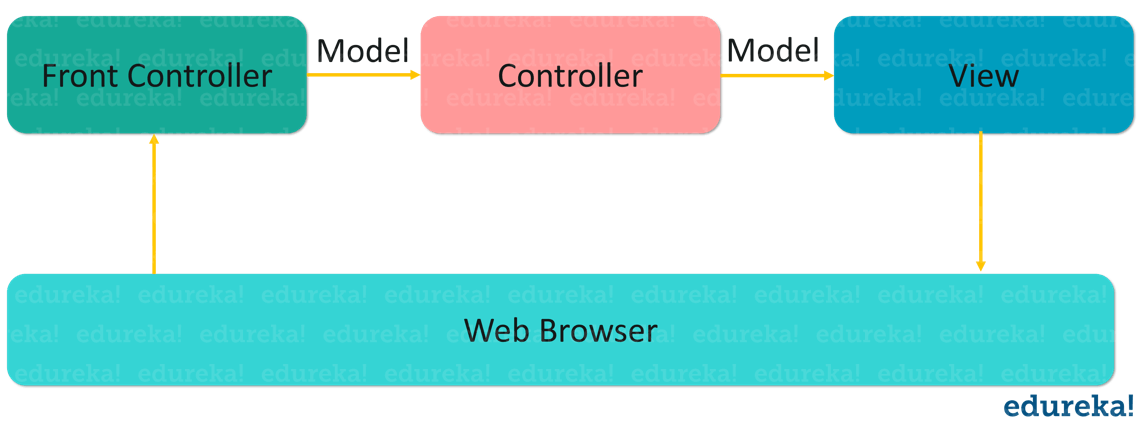 2. Explain what is MVC?
2. Explain what is MVC?
MVC is an abbreviation for Model, View, and Controller. The MVC architectural pattern separates an application into three components – Model, View, and Controller. In this pattern, the model represents the shape of the data and business logic. It maintains and preserves the data of the application. Model objects retrieve and store model state in a database. The view is basically and technically a user interface. The view segment displays the data-using model to the user and also enables them to modify the data. The controller is the part, which handles the user request.
View Result
Javascript Result
Redirect Result
JSON Result
Content Result
Benefits or the advantages of MVC are as follows:
Multiple view support: Because of the separation of the model from the view, the user interface can display multiple views of the same data and at the same time.
Change Accommodation: User interfaces tend to change more frequently than business rules.
SoC – Separation of Concerns: Separation of Concerns is one of the core advantages of ASP.NET MVC. The MVC framework provides a clean separation of the UI, Business Logic, Model or Data.
More Control: The ASP.NET MVC framework provides more control over HTML, JavaScript, and CSS than the traditional WebForms.
Testability: This framework provides better testability of the Web Application and good support for the test-driven development too.
Lightweight: MVC framework doesn’t use View State and that reduces the bandwidth of the requests to an extent.
Presentation: It is the visual representation of a specific abstraction within the application.
Abstraction: It is the business domain functionality within the application.
Control: It is a component that keeps consistency between the abstraction within the system and their presentation to the user. It is also used to communicate with other controls within the system.
The session can be maintained in MVC by three ways temp data, viewdata, and view bag.
Any web application has two main execution steps, first understanding the request and depending on the type of the request, sending out an appropriate response. MVC application life cycle has two main phases, first creating the request object and second sending the response to the browser.
Creating the request object includes four basic steps:
Step 1: Fill route
Step 2: Fetch route
Step 3: Request context created
Step 4: Controller instance created
The MVC model defines web applications with 3 logic layers:
The business layer (Model logic)
The display layer (View logic)
The input control (Controller logic)
The Model is the part of the application, which only handles the logic for the application data. Regularly, the model objects retrieve data (as well as store data) from a database. The View is the part of the application, which takes care of the display of the data. Most often, the views are created from the model data, although there are other, more complicated methods of creating views. The Controller, as the name implies, is the part of the application that handles user interaction.
It is a Java framework which is used to build web applications. It follows the Model-View-Controller design pattern. Not just that, it also implements all the basic features of a core Spring Framework like Inversion of Control, Dependency Injection. Spring MVC provides a dignified solution to use MVC in Spring Framework by the help of DispatcherServlet. In this case, DispatcherServlet is a class that receives the incoming request and maps it to the right resource such as Controllers, Models, and Views.
ASP.NET MVC is a web application Framework. It is lightweight and highly testable Framework. MVC separates an application into three components — Model, View, and Controller.
The URLs in ASP.NET MVC are mapped to action methods and controller instead of physical files of the system. To accurately map action methods and controller to URLs, the routing engine forms appropriate routes. Using this, the controllers can handle specific requests.
 12. What are the Filters?
12. What are the Filters?Sometimes we want to execute some logic either before the execution of the action method or after the execution. We can use Action Filter for such kind of scenario. Filters define the logic which is executed before or after the execution of the action method. Action Filters are attributes which we can apply to the action methods. Following are the MVC action filter types:
Authorization filter (implements IAuthorizationFilter)
Action filter (implements IActionFilter)
Result filter (implements IResultFilter)
Exception filter (implementsIExceptionFilter attribute)
A partial view is a chunk of HTML that can be safely inserted into an existing DOM. Most commonly, partial views are used to componentize Razor views and make them easier to build and update. It can also be returned directly from controller methods. In this case, the browser still receives text/HTML content but not necessarily HTML content that makes up an entire page. As a result, if a URL that returns a partial view is directly invoked from the address bar of a browser, an incomplete page may be displayed. This may be something like a page that misses title, script and style sheets.
Below mentioned steps define the page life cycle.
App initialization
Routing
Instantiate and execute controller
Locate and invoke controller action
ViewModel is a plain class with properties, which is used to bind it to a strongly-typed view. ViewModel can have the validation rules defined for its properties using data annotation.
Database First Approach is an alternative or substitutes to the Code First and Model First approaches to the Entity Data Model. The Entity Data Model creates model codes (classes, properties, DbContext, etc.) from the database in the project and that class behaves as the link between database and controller.
There are the following approaches, which are used to connect the database with the application.
Database First
Model First
Code First
Scaffolding is a code generation framework for ASP.NET Web applications. Visual Studio includes pre-installed code generators for MVC and Web API projects. You add scaffolding to your project when you want to quickly add the code that interacts with data models. Using scaffolding can reduce the amount of time to develop standard data operations in your project.
It consists of page templates, entity page templates, field page templates, and filter templates. These templates are called Scaffold templates and they allow you to quickly build a functional data-driven Website.
ASP.NET MVC has always supported the concept of “view engines” – which are the pluggable modules that implement different template syntax options. The “default” view engine for ASP.NET MVC uses the same .aspx/.ascx/. master file templates as ASP.NET WebForms. Other popular ASP.NET MVC view engines are Spart & Nhaml. Razor is the new view-engine introduced by MVC 3.
Default Route: The default ASP.NET MVC project templates add a generic route that uses the following URL convention to break the URL for a given request into three named segments.
URL: "{controller}/{action}/{id}"
This route pattern is registered via a call to the MapRoute() extension method of RouteCollection.
GET Action Type: GET is used to request data from a specified resource. With all the GET requests, we pass the URL, which is compulsory; however, it can take up the following overloads.
POST Action Type: Tthe POST is used to submit data to be processed to a specified resource. With all the POST requests, we pass the URL, which is essential and the data. However, it can take up the following overloads.
View Data | View Bag |
ViewData is used to pass data from a controller to view | ViewBag is also used to pass data from the controller to the respective view. |
It is available for the current request only. | It is also available for the current request only. |
Requires typecasting for complex data type and checks for null values to avoid error | Doesn’t require typecasting for the complex data type. |
If redirection occurs, then its value becomes null. | If redirection occurs, then its value becomes null. |
Benefits of Area in MVC are as follows:
It allows us to organize models, views, and controllers into separate functional sections of the application, such as administration, billing, customer support and much more.
It is easy to integrate with other Areas created by another.
Also, easy for unit testing.
In the end “Exception Filters” are executed.
Two methods for adding constraints to the route is
Using regular expressions
Using an object that implements IRouteConstraint interface
We can easily implement validation in MVC application by using the validators defined in the System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations namespace. There are different types of validators as follows:
Required
Range
StringLength
Two instances where routing is not required are:
When a physical file is found that matches the URL pattern
When routing is disabled for a URL pattern
In MVC, Ajax can be implemented in two ways. They are as follows:
Ajax libraries
Once “TempData” is read in the current request, it’s not available in the subsequent request. If we want “TempData” to be read and also available in the subsequent request then after reading we need to call “Keep” method as shown in the code below.
@TempData["MyData"];
TempData.Keep("MyData");The more shortcut way of achieving the same is by using “Peek”. This function helps to read as well advices MVC to maintain “TempData” for the subsequent request.
string str = TempData.Peek("Td").ToString();HTTP is the most used protocol. Since many years, the browser was the most preferred client by which we consumed data exposed over HTTP. But as years passed by, client variety started spreading out. We had demanded to consume data on HTTP from clients like mobile, JavaScript, Windows applications, etc.
For satisfying the broad range of clients, REST was the proposed approach. WebAPI is the technology by which you can expose data over HTTP following REST principles.
To detect if the call on the controller is a POST action or a GET action we can use the Request.HttpMethod property as shown in the below code snippet.
public ActionResult SomeAction(){
if (Request.HttpMethod == "POST"){
return View("SomePage");
}
else{
return View("SomeOtherPage");
}
}Now let’s move further and look at the Advanced MVC Interview questions.
Following are the rules for main Razor Syntax:
Razor code blocks are enclosed in @{ … }
Inline expressions (variables and functions) start with @
Code statements end with a semicolon
Variables are declared with the var keyword
Strings are enclosed with quotation marks
C# code is case sensitive
C# files have the extension .cshtml
Authentication is giving access to the user for a specific service by verifying his/her identity using his/her credentials like username and password or email and password. It assures that the correct user is authenticated or logged in for a specific service and the right service has been provided to the specific user based on their role.
RenderBody is like ContentPlaceHolder in web forms. This will exist in layout page and it will render the child pages/views. Layout page will have only one RenderBody() method. RenderPage also exists in Layout page and multiple RenderPage() can be there in the Layout page.
In MVC all public methods have been treated as Actions. So if you are creating a method and if you do not want to use it as an action method then the method has to be decorated with “NonAction” attribute as shown below –
[NonAction]
public void TestMethod(){
// Method logic
}In the controller, you can override the “OnException” event and set the “Result” to the view name which you want to invoke when an error occurs. In the below code you can see we have set the “Result” to a view named as “Error”.
We have also set the exception so that it can be displayed inside the view.
public class HomeController : Controller{
protected override void OnException(ExceptionContext filterContext){
Exception ex = filterContext.Exception;
filterContext.ExceptionHandled = true;
var model = new HandleErrorInfo(filterContext.Exception, "Controller","Action");
filterContext.Result = new ViewResult()
{
ViewName = "Error",
ViewData = new ViewDataDictionary(model)
};
}
}As per Microsoft, Razor is more preferred because it’s lightweight and has simple syntax’s.
Unlike code expressions that are evaluated and sent to the response, it is the blocks of code that are executed. This is useful for declaring variables which we may be required to be used later.
@{
int x = 123;
string y = “aa”;
}This method is used to render the specified partial view as an HTML string. This method does not depend on any action methods. We can use this like below –
@Html.Partial(“TestPartialView”)
Glimpse is NuGet packages which help in finding performance, debugging and diagnostic information. Glimpse can help you get information about timelines, model binding, routes, environment, etc.
By using the ActionLink method you can navigate. The below code will create a simple URL which helps to navigate to the “Home” controller and invoke the Gotohome action.
<%= Html.ActionLink("Home","Gotohome") %>This brings us to the end of this article on MVC Interview Questions. Hope it helped in adding up to your knowledge. Wishing you all the best for your interview. Happy learning.
Check out the online training by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. We are here to help you with every step on your journey through our online certification training.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of this “MVC Interview Questions” article and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
| Course Name | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| Java Certification Training Course | Class Starts on 28th January,2023 28th January SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
| Java Certification Training Course | Class Starts on 25th February,2023 25th February SAT&SUN (Weekend Batch) | View Details |
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR  Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
edureka.co
